Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following products is most likely to
have an elastic demand?
a. | toothpicks | b. | insulin | c. | cigarettes | d. | automobiles |
|
|
|
2.
|
An increase in the wages of construction workers
will:
a. | shift the demand curve for construction workers to the
right | b. | lead to an increase in the quantity supplied of new
homes | c. | shift the supply curve of new homes to the
left | d. | decrease the average annual incomes of construction
workers |
|
|
|
3.
|
In which of the following instances does total
revenue increase?
a. | price falls and demand has
unitary-elasticity | b. | price falls and
supply is inelastic | c. | price rises and
demand is inelastic | d. | price rises and
demand is elastic |
|
|
|
4.
|
Price ceilings and price floors:
a. | make the functioning of free markets more
efficient | b. | alwyas cause shortages | c. | interfere with the efficient operations of free
markets | d. | shift demand and supply
curves |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which statement about quotas is
true?
a. | A max. quota greater than equilibrium quantity will
create a surplus. | b. | A max quota set
below equilibrium quantity will reduce the amount that a free market would choose to produce, would
thus create the incentive for suppliers to break quotas, produce for a black market, and society will
pay far more than necessary on legitimate markets, destroying the consumer surplus
| c. | A min. quota set below equilibrium would create
shortages and result in black markets for goods and huge losses for suppliers as they must offer
artificially low prices in order sell unwanted goods, destroying the producer
surplus. | d. | A min. quota set above equilibrium has no
effect. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which statement about sales taxes and subsidies is
true?
a. | Taxes will always raise demand for a product
| b. | Subsidies create surpluses. | c. | No single side of the market can keep all the benefit of a subsidy or pay all
the cost of a tax; it will be shared between consumers and suppliers. | d. | Taxes and subsidies will always result in inefficient markets that have
shortages or surpluses. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The price elasticity of demand
indicates:
a. | the extent to which a demand curve shifts as income
changes | b. | the extent to which consumers respond to a change in
price | c. | the length of the demand
curve | d. | how far business executives can stretch their fixed
costs |
|
|
|
8.
|
An elastic demand curve is one for
which:
a. | the change in price is equal to the change in quantity
demanded | b. | a given percentage change in price causes a smaller
percentage change in quantity demanded | c. | the change in
revenue is bigger than the change in quantity demanded | d. | a given percentage change in price causes a larger percentage change in
quantity demanded |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following does not cause the demand
for product K to change?
a. | an increase in consumer
incomes | b. | a change in the price of K | c. | a change in consumer preferences | d. | a change in the price of substitute product
J |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following affects the steepness of the
slope of a demand curve?
a. | costs | b. | tastes and preferences | c. | income levels
among consumers | d. | customes and
cultural values |
|
|
|
11.
|
The price elasticity of supply measures
how:
a. | responsive the quantity supplied of X is to changes in
the price of X | b. | responsive
quantity supplied is to a change in incomes | c. | responsive the
quantity supplied of Y is to changes in the price of X | d. | easily labour and capital can be substituted for one another in the production
process |
|
|
|
12.
|
Price floors and price ceilings:
a. | both cause surpluses | b. | both cause shortages | c. | Price floors cause
surpluses and price ceilings cause shortages | d. | cause the supply
and demand curves to shift until equilibrium is established |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.
|
Looking at the demand curve above, at Price = $15, what is the elasticity
coefficient for a price increase of $2?
a. | 1.875 | b. | -2/5 | c. | -0.533 | d. | -1.875 | e. | -0.353 | f. | -2.833 | g. | The answer is not on
this list |
|
|
|
14.
|
If the elasticity of demand is -3, this means
a. | Demand is falling | b. | The demand curve is elastic at this particular
point | c. | Demand will rise at three times the rate that price rises | d. | The demand line is
elastic |
|
|
|
The following questions deal with this graph below.
NOTE: The
questions are less memorized knowledge, and more understanding of graphing and concepts. This
requires some Thinking/Inquiry (i.e. analysis) as well.
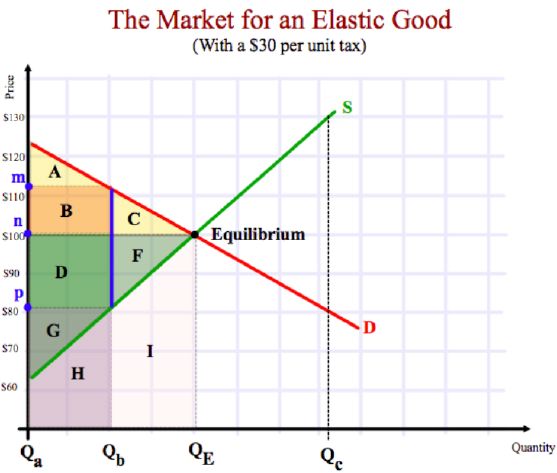 Pop
out this graph Pop
out this graph
|
|
|
15.
|
What area represents the consumer surplus before the tax?
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the producer surplus before the tax?
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the price level without any government interference?
|
|
|
18.
|
What price do consumers pay after the tax has been introduced?
|
|
|
19.
|
What price do producers receive after the tax is introduced?
|
|
|
20.
|
If producers tried to pass on all of the $30 tax to consumers what would be the
quantity demanded?
a. | Unknown | b. | Qa | c. | Qb | d. | QE | e. | Qc |
|
|
|
21.
|
If producers were able to pass on all of the tax to consumers, what would be the
quantity supplied?
a. | Unknown | b. | Qa | c. | Qb | d. | QE | e. | Qc |
|
|
|
22.
|
What area represents the amount of tax collected by the government?
a. | BDGH | b. | N times Qb | c. | BD | d. | GH | e. | DFGHI |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the revenue received by just the industry (not the government) after the
tax is imposed?
|
|
|
24.
|
What area represents how much less revenue the industry receives now that
there’s a tax on this product?
|
|
|
The next questions refer to the graphical illustration below. It represents
these two events:
(a) Suppliers are not able to increase their maximum output. However, as
time passes, producers become successful in expanding capcity, as well as in building warehousing
facilities and improving distribution networks.
(b) Income levels are rising and this
developing country’s preference for wearing western-style jeans is rising. 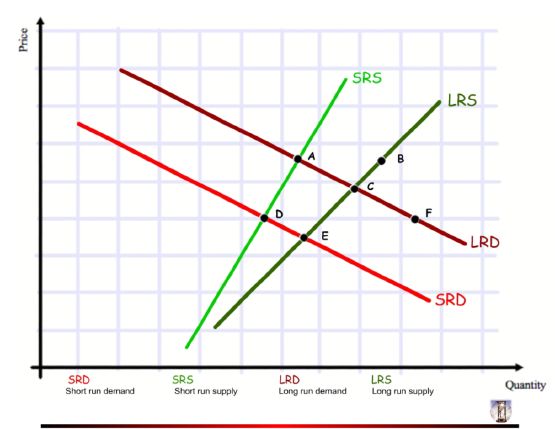 Pop
out this graph. Pop
out this graph.(Need help? Try here.)
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following is the first shock?
a. | Prices are raised as sellers witness more demand for their
product. | b. | Quantity supplied rises as sellers try to produce more product since the price went
up. | c. | (i) Preferences and (ii) wealth shift the demand curve to the right because consumers
(i) want more and (ii) can afford more at all price levels. | d. | (i) Increased output
and more producers shift the supply curve, and (i) better distribution and warehousing change time to
market and increase suppliers responsiveness (i.e. lowers slope/increases
elasticity). |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is the second shock?
a. | Prices are raised as sellers witness more demand for their
product. | b. | Quantity supplied rises as sellers try to produce more product since the price went
up. | c. | (i) Preferences and (ii) wealth shift the demand curve to the right because consumers
(i) want more and (ii) can afford more at all price levels. | d. | (i) Increased output
and more producers shift the supply curve, and (i) better distribution and warehousing change time to
market and increase suppliers responsiveness (i.e. lowers slope/increases
elasticity). |
|
|
|
27.
|
What will the end result (in the long-run) of all of the forces and market
shocks described in the graph?
a. | The equilibrium Quantity rises, and the market Price falls | b. | The equilibrium
Quantity falls, and the market Price rises | c. | The equilibrium Quantity rises, and the market
Price rises | d. | The equilibrium Quantity falls, and the market Price
falls |
|
|
|
28.
|
What letter corresponds to the initial equilibrium of the jean market in this
developing economy?
a. | A | b. | B | c. | C | d. | D | e. | E | f. | F | g. | Not
shown |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which letter corresponds to the price/quantity demanded point of the jean
market after its first “shock”?
|
|
|
30.
|
Which letter corresponds to the price/quantity supplied point of the jean
market after its first “shock”?
|
|
|
31.
|
If a new equilibrium is reached before the second shock, where would it
be?
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the price/quantity demanded point immediately after the second
shock?
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the price/quantity supplied point immediately after the second
shock?
|
|
|
34.
|
Where is the final equilibrium after all events described have taken place?
|
Matching - NOTE: Not all terms will be
used.
|
|
|
a. | Utility | k. | Price
floor | b. | Surplus | l. | Price
ceiling | c. | Shortage | m. | Quota | d. | Shift in demand
curves | n. | Marginal benefit | e. | Equilibrium
price | o. | Consumer surplus | f. | Law of demand and
supply | p. | Substitute good | g. | Demand
curve | q. | Complementary good | h. | Quantity
supplied | r. | Law of diminishing marginal utility | i. | Market demand | s. | Price elasticity of demand | j. | Inferior good | t. | Inelastic demand |
|
|
|
35.
|
The difference between total benefit and total
expenditure for a given quantity of a product
|
|
|
36.
|
The responsiveness of a product's quantity
demanded to a change in its price
|
|
|
37.
|
The legal minimum price set above
equilibrium
|
|
|
38.
|
A good whose increase in price increases demand
for another good
|
|
|
39.
|
The sum of all consumers' quantity demanded
for a product at each price
|
|
|
40.
|
The price at which quantity demanded equals
quantity supplied
|
|
|
41.
|
The number of units that producers want to sell at
a given price
|
|
|
42.
|
The legal maximum price set below
equilibrium
|
|
|
43.
|
The excess of quantity demanded over
quantity supplied
|
|
|
44.
|
The excess of quantity supplied over
quantity demanded
|
|
|
45.
|
The theory that additional units of a particular
product generally have a decreasing value to the consumer
|
|
|
46.
|
A legal limit set by the government on the
production of a product
|
|
|
47.
|
A good whose increase in price decreases demand
for another good
|